Banking Resolution
Resolution is the restructuring of a failed credit institution or investment firm, or of one that will fail in the near future, when no alternatives exist or whereby it is necessary on grounds of public interest and financial stability to avoid it going into liquidation.
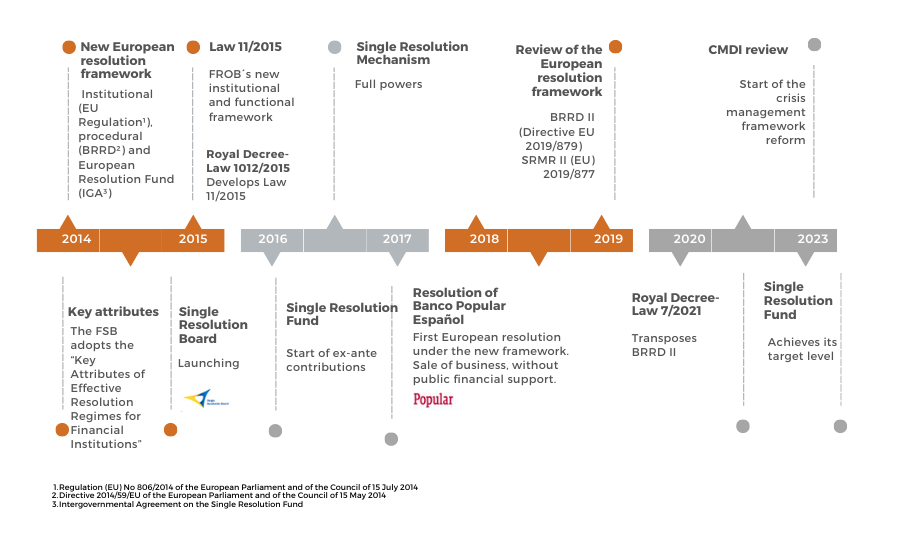
The impact of the financial crisis that began in 2008 on the taxpayer and on financial stability revealed the limits of the existing crisis management regulatory framework. For this reason, the European Union approved the regulatory framework for banking resolution (the Resolution Directive and the Regulations that develop it), implementing the new international standards agreed by the Financial Stability Board.
At national level, Law 11/2015 developed the new institutional framework in Spain, establishing a new paradigm in the management of banking crises: the principle that shareholders and then the creditors must assume losses in the event of a resolution, with the goal of protecting financial stability and the taxpayer.
The European framework was revised in 2019, with the aim of reinforcing it by implementing international loss absorption and recapitalization standards and by giving resolution authorities powers to analyse the progress of entities in facilitating their resolution, along with sanctioning capabilities.
On April 18th, 2023, the European Commission published a new proposal to reform the crisis management framework. This proposal pays more attention to an efficient resolution of crises in small and medium-sized entities.